What You Know About Cannabidivarin – CBDV?
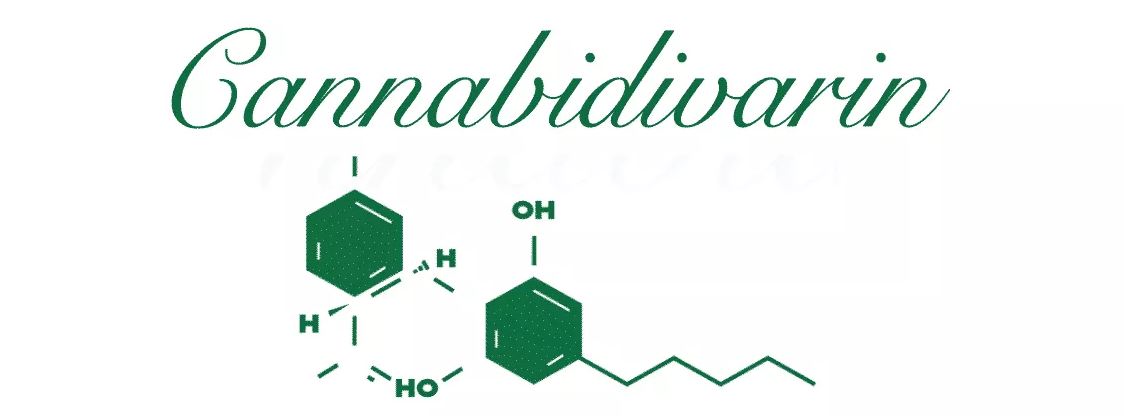 Cannabidivarin is one of the many known cannabinoids. It is non-psychoactive cannabinoid that is similar to CBD in molecular structure. Both of these cannabinoids are medicinal. Since psychoactive compounds are illegal, the laws have restricted or limited the therapeutic research and public access to all non-psychoactive cannabinoids.
Cannabidivarin is one of the many known cannabinoids. It is non-psychoactive cannabinoid that is similar to CBD in molecular structure. Both of these cannabinoids are medicinal. Since psychoactive compounds are illegal, the laws have restricted or limited the therapeutic research and public access to all non-psychoactive cannabinoids.
Fortunately, with time, there have been discoveries of several other cannabinoids that are actually non-psychoactive and contain a high amount of healing properties of cannabis. Even though there is a limitation of research, some studies conclude that cannabidivarin contain nausea relieving and anticonvulsive properties.
Exploring Cannabidivarin
Cannabidivarin – CBDV is a homolog of CBD. This means that it contains similar molecular structure. Just like CBD, cannabidivarin also contains 7 double bond isomers along with 30 stereoisomers.
Another major similarity between CBDV and CBD is that both of them are non-psychoactive. Hence, any patient suffering from anxiety and also sensitive to THC high levels can continue to enjoy some great benefits without experiencing panic-inducing high.
If you would go to a dispensary, you can easily find strains of cannabidivarin. Strains which contain higher CBD levels also tend to have a higher CBDV level. Indeed, most of the strains nowadays are bred to contain a high level of terpenes and THC.
Plants having higher cannabidivarin levels are majorly found in Pakistan, India and Mexico.
Medical Potential of Cannabidivarin – CBDV
Botanical extracts rich in CBDV have shown to contain strong anticonvulsive properties in rats and mice. They are also recognized to suppress the expression of various genes associated to epilepsy.
In 2014, the team of researchers studied that THC and CBD effects on rats, having induced epilepsy symptoms. They observed that both of the non-psychoactive cannabinoids successfully interacted with the TRPV1 – transient receptor.
TRPV1 is highly responsive to detect and regulate body temperature while producing pain sensations.
The anticonvulsive medicine Capsaicin combats the steady process through which our normal brain develops epilepsy by targeting TRP channels. The research team found Capsaicin dephosphorylated TRPV1 and CBDV. They further proposed to study the effects of CBDV on TRP channels to completely understand the anticonvulsive abilities of cannabinoids.
The study found CBDV reduced the strength and length of simulated epileptic seizures in the brains of rats.
While there is still need for an abundance of research on CBDV out there, the anticonvulsant abilities of cannabinoid are proved in many studies. CBD is also known to treat seizures and nausea from debilitating conditions such as epilepsy – as per multiple studies.
A study was conducted in 2013, in which it was found that CBDV remarkably reduced PTZ-induced severity of seizures and enhanced latency to the seizure’s first sign.
The authors stated that such results gave the first molecular confirmation in terms of behaviorally observed effects of the anticonvulsant, non psychoactive cannabinoid – CBDV – upon seizures (chemically-induced), and serve to underscore CBDV sustainability for further clinical development.
Nonetheless, cannabidivarin is among hundreds of other similar cannabinoids identified so far. It has great tendency to interact with pain receptors just like all other cannabinoids.