THCA-B – Delta-9- tetrahydrocannabinolic acid B – A nonpsychoactive acidic form of THC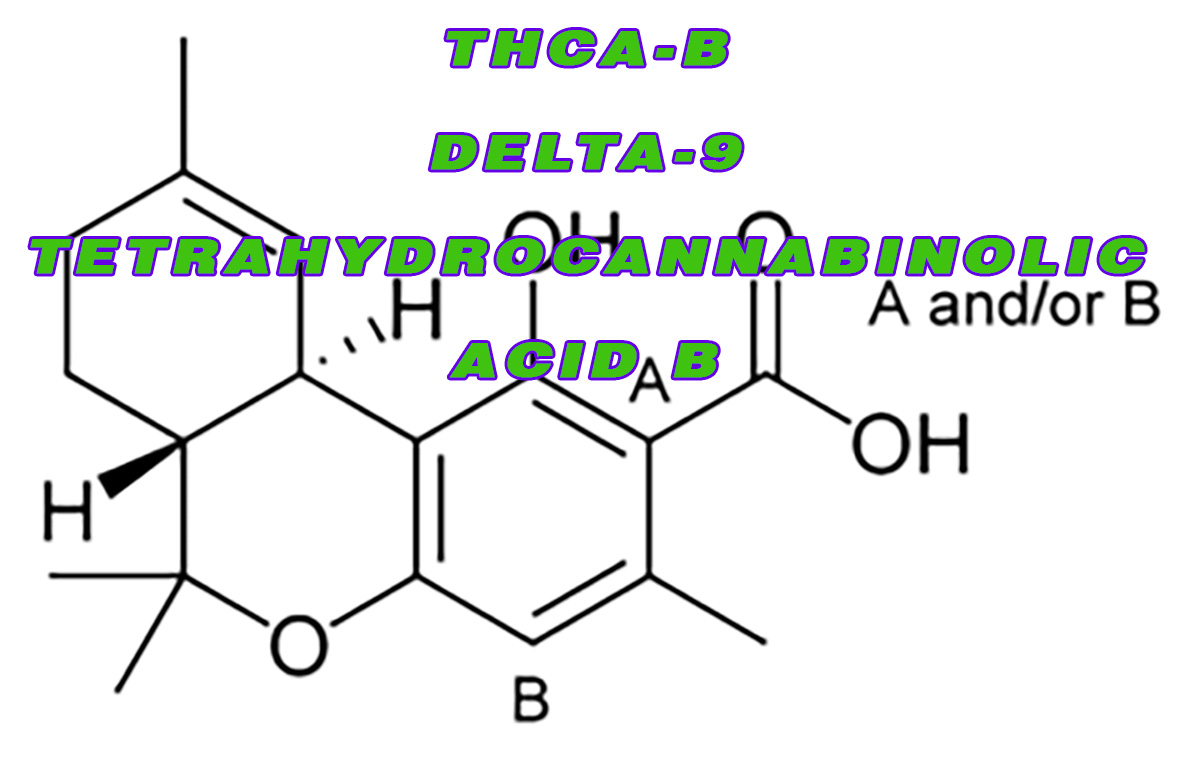
The molecular and crystal structure of the compound THCA-B – Delta-9- tetrahydrocannabinolic acid B, was determined by using X-ray methods. It was determined by using around 1106 reflections above the background level which were collected by counter methods. The crystals are known to be orthorhombic and there are exactly four molecules in each unit cell.
Speaking of tetrahydrocannabinolic acid or THCA, the term has always been hazily used (in the literature) to refer numerous acidic derivatives of tetrahydrocannabinol or THC. This makes it confusing to explicitly individuate their pharmacological and physiological profile.
Back in 1965, Friedhelm Korte, a renowned professor from the University of Bonn was the first person who identified tetrahydrocannabinol carboxylic acid as one of the major components of hashish. After four years, in 1969, Raphael Mechoulam from the University of Jerusalem found and reported the 2nd THC acid – the isomer 4-carboxy-THC. He named the former THCA – A – tetrahydrocannabinolic acid A and the latter as THCA-B or tetrahydrocannabinolic acid B.
The latter THC acid i.e. THCA-B – Delta-9- tetrahydrocannabinolic acid B was only present in hashish samples that contained quite less or even no tetrahydrocannabinolic acid – A. Even the general or overall concentrations of THCA-B were found lower than 0.5 percent in weight.
THCA-B – Delta-9- Tetrahydrocannabinolic Acid B Has Greater Stability
Cannabis generally biosynthesizes cannabinoids more like carboxylic acids. In fact, the carboxylic acid associated with delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol – THC is delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinolic acid – THCA. So far and as stated earlier, two isomers related to THCA have been explored. These include 2-COOH-THC (THCA-A) and 4-COOH-THC (THCA-B).
After the much-needed research work, it was found that cannabis first biosynthesizes THCA-A. In fact, this isomer was the main focus of many pharmacological studies. On the other hand, tetrahydrocannabinolic acid B possess greater stability. THCA-B crystallizes much more readily than the former THCA-A. This makes THCA-B, an important molecule for major modeling studies of several cannabinoid receptors.
As per the canonical cannabinoid biosynthesis; olivetolic acid is primarily prenylated into CBGA or cannabigerolic acid with the carboxylic acid in an ‘A’ position. THCA-B also shows greater thermal stability in comparison to THCA-A. Therefore, it is worth investigation. Even though only two studies have quantified both THCA-A and THCA-B content in a range of cannabis landraces, the prevalence of THCA-B – Delta-9- tetrahydrocannabinolic acid B is relatively unknown.
THCA Highlights
THCA is the nonpsychoactive acidic form of THC that is found in the raw cannabis plant. There are many laboratory and clinical studies that show promising effects of THCA for the treatment of chronic pain, epilepsy, digestive disorders and others.
As a matter of fact, cannabis plant doesn’t produce tetrahydrocannabinol on their own but they create cannabinoids in a more acid form. In order to convert THCA into a more psychoactive THC, it needs to be first heated. For instance, by smoking or vaping.
THCA shows promising results in the treatment of many chronic diseases. While we still face lack of funding for research work due to marijuana legalization issue, we can only put what we know in our perspective though.