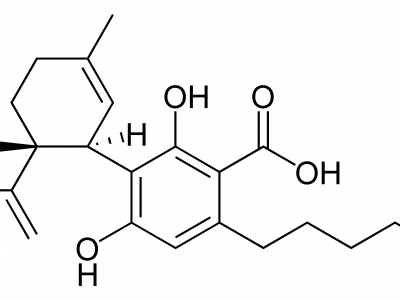
Cannabichromene Acid – A Naturally Occurring Cannabinoid
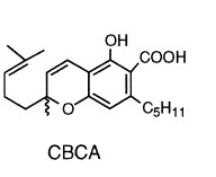 Back in 2015, scientists from University of Mississippi discovered seven naturally occurring new cannabinoids. As reported in the scientific literature, now there are almost 111 recognized natural cannabinoids.
Back in 2015, scientists from University of Mississippi discovered seven naturally occurring new cannabinoids. As reported in the scientific literature, now there are almost 111 recognized natural cannabinoids.
Among these distinctive cannabinoids, Cannabichromene acid (CBC-a) is one the major cannabinoid present in the cannabis plant. Cannabichromene acid is considered as the fourth key cannabinoid. CBC-a is typically located, in the richest levels, in marijuana tropical plant strains. While it is also found in some other strains, it might not be present in the most abundant levels.
What are the benefits of Cannabichromenic Acid?
Well, in recent years, certain marijuana strains have been discovered or developed which boast much higher than normal CBC-a levels. The pharmaceutical industry and medical marijuana researchers have found that such strains containing higher CBC-levels are capable to fight off inflammation as well as hold some amazingly strong antibacterial properties.
These medical benefits of Cannabichromenic Acid – CBC-a were not known long before. These are recent research findings that provide strong evidence of such medical implications.
Characterization and Purification of Cannabichromenic Acid synthase from Cannabis
Cannabichromenic acid synthase is purified to specific yet apparent homogeneity using sequential column chromatography that includes phenyl-Sepharose CL-4B, DEAE-cellulose, and hydroxylapatite.
The enzyme then catalyzed the cannabinerolic acid and oxidocyclization of cannabigerolic acid to cannabichromenic acid. The values K(m) for both of these substrates were kept in the same order of magnitude whereas Vmax value of the later was higher than that of the former.
The study suggested that the cannabichromenic acid is largely created from cannabigerolic acid than cannabinerolic acid. The enzyme did not require hydrogen peroxide or molecular oxygen which mean that the synthase reaction of cannabichromenic acid proceeds without hydroxylation and through direct dehydrogenation.
CBC-a Binds with the C-receptors in the Human body
 Cannabichromenic acid is assumed to start being secreted from the cannabis plant during the early seeding stage. It appears that cannabichromenic acid grows in the young seeding even before this young plant starts to develop tetrahydrocannabinol – THC.
Cannabichromenic acid is assumed to start being secreted from the cannabis plant during the early seeding stage. It appears that cannabichromenic acid grows in the young seeding even before this young plant starts to develop tetrahydrocannabinol – THC.
CBC-a is non-psychoactive that is unlike THC. Through heating and aging process, later it can be transformed into CBC – Cannabichromene. This heating process is referred as decarbing or decarboxylation. It converts the CBC-a into a more usable CBC that readily binds with the C-receptors inside the human body.
CBCA helps fight pain, bacteria and helps in brain growth. The vaporization temperature of this cannabichromene is 212 degrees Fahrenheit to 292 degrees Fahrenheit.
Just like CBC-a, the other four highly sought-after cannabinoids; CBD, CBC, CBG, and THC are all gained via decarbing process. All of them are highly important cannabichromene. These big four cannabichromene compounds are being tested and studied by many researchers to know their wide-scale possible medicinal benefits.
CBC-a plays a crucial role in the anti-viral and anti-inflammatory effects of cannabis. This also contributes to the overall analgesic effects relating to medical cannabis. It offers anti-depressant effects and helps promote neurogenesis.
Conclusively, there are numerous studies and research reports that provide a better understanding with regards to the participation of such chemical compounds to the antidepressant action of cannabis as a whole.