What You Need to Know About Myrcene
Myrcene is the smallest of the terpenes – monoterpene – and is found abundantly (in high concentrations) in hops, sweet basil, mangoes and of course cannabis. It possesses an earthy and fruity odor and can be very pungent in high concentrations such as heavily hopped beer.
To your surprise, cannabis and hops are cousins and belong to the family of Cannabaceae. Myrcene got its name from a medicinal shrub found in Brazil. This shrub is known to contain a very high concentration of Myrcene that has been used for decades as a folk remedy to treat dysentery, diabetes, hypertension, and diarrhea.
A study was conducted in the year 1997 in Switzerland in which various cannabis strains were analyzed for 16 terpenes.
Among them, Myrcene was found to be the most abundant terpene among all of them. Other found terpene includes Limonene, Pinene, Humulene, Carene, Terpinolene, Bergamotene, and Caryophyllene. In some strains, the content of Myrcene was more than half the total content of terpene.
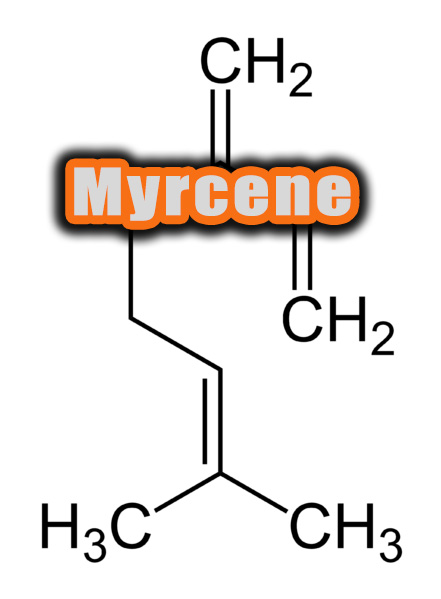
Chemical Formation of Myrcene
Myrcene has the molecular formula of C10H16. It has the molecular weight of 136.238 g/mol. It exists in the liquid form and considered to be insoluble in water.
It is relatively neutral and has been detected in several biofluids such as saliva and feces. In a cellular structure, Myrcene is found in the membrane as well as cytoplasm.
It exists in all types of eukaryotes, ranging from humans to yeast. Potentially, Myrcene is a toxic compound. As per the Steep Hill Labs, if a person eats mango at least 45 minutes earlier than inhaling cannabis, this will increase the cannabis effects.
Myrcene and the Therapeutic Effects

Following are some therapeutic uses of Myrcene.
- Analgesic – helps to relieve pain
- Antibacterial – slows down bacterial growth
- Anti-diabetic which helps in mitigating the diabetes effects
- Anti-inflammatory – systemically reduces inflammation
- Anti-insomnia – aiding the sleep pattern
- Antipsychotic – produces tranquilizing effects and help in relieving the psychosis symptoms
- Antispasmodic – suppresses the muscle spasm
These are some of the well known therapeutic effects of Myrcene. However, the compound is still being studied for numerous other symptoms.
For instance, Myrcene is known to produce barbiturate-like strong sedative effects in mice. But, in very high doses than usual, considering the study conducted in 2002. It was observed that the effects increase when citrial, a proper mixture of some other terpene, is present as well.
Similarly, the neurobehavioral effects of Myrcene are also studied on mice. These include anti-anxiety and anti-depressant effects. As per the results, Myrcene possesses strong sedative and analgesic effects but it created no impact on cutting down depression, anxiety or psychosis. In fact, as per one of the studies conducted in 2002 and published in Journal of Phytomedicine, high doses of myrcene may actually increase the anxiety effects than reducing it.
While the research work on myrcene is still going on, there is still some time to fully recognize and understand the effects of this easily available terpene on human beings.